In the digital world, design is crucial in how businesses communicate with their audiences. Whether creating a website, developing a mobile app, or crafting marketing materials, the design approach varies significantly between Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Business-to-Business (B2B) contexts. Understanding these differences is essential for designers and businesses alike to effectively engage their target audiences.
💠Audience and User Persona
- B2C Design: Emphasizes user engagement by incorporating interactive elements, gamification, and innovative features, with loyalty programs and personalized experiences being standard practices.
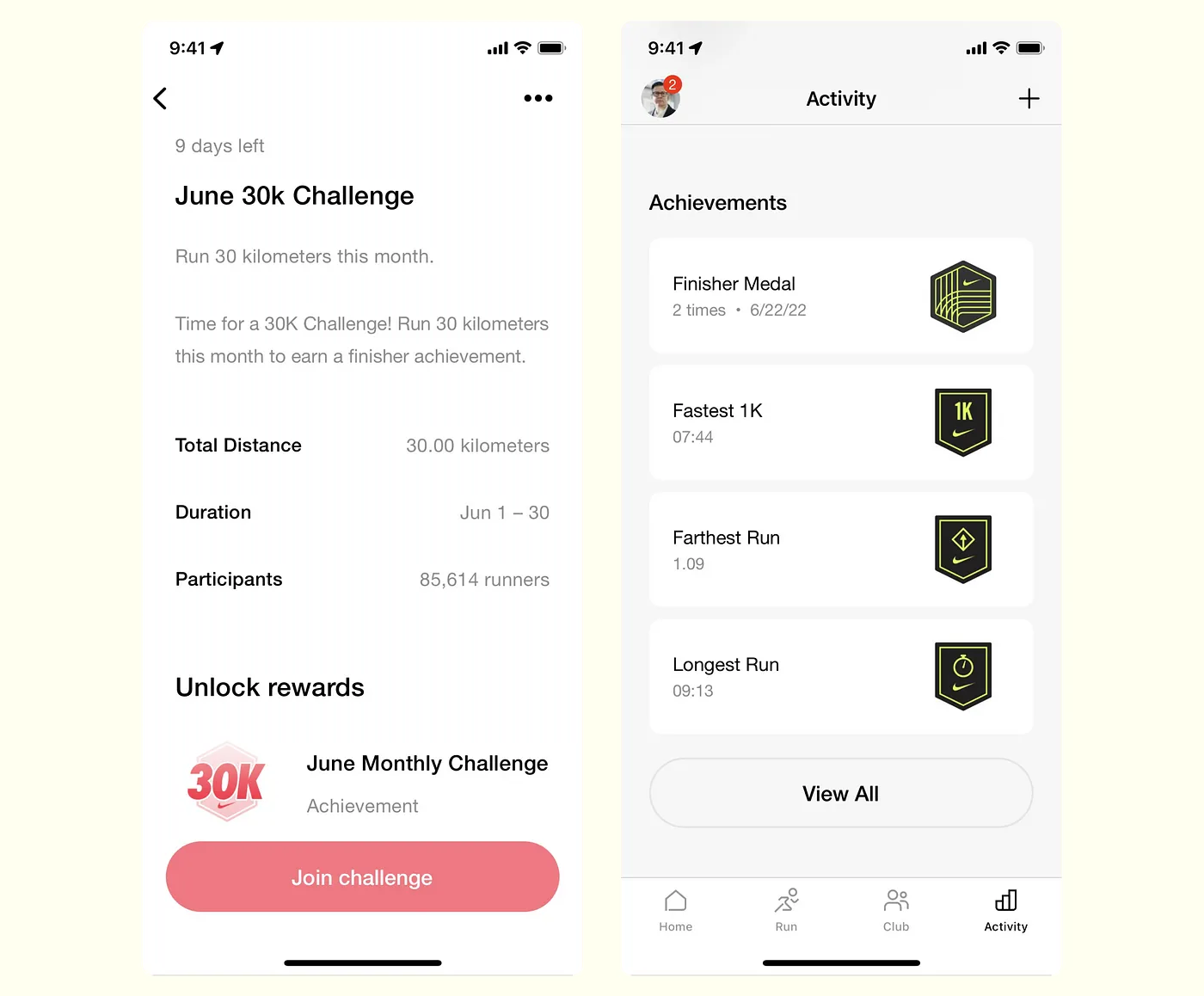
- B2B Design: Business-to-business strategies focus on establishing long-term relationships and maintaining consistent engagement by delivering reliable performance and value.
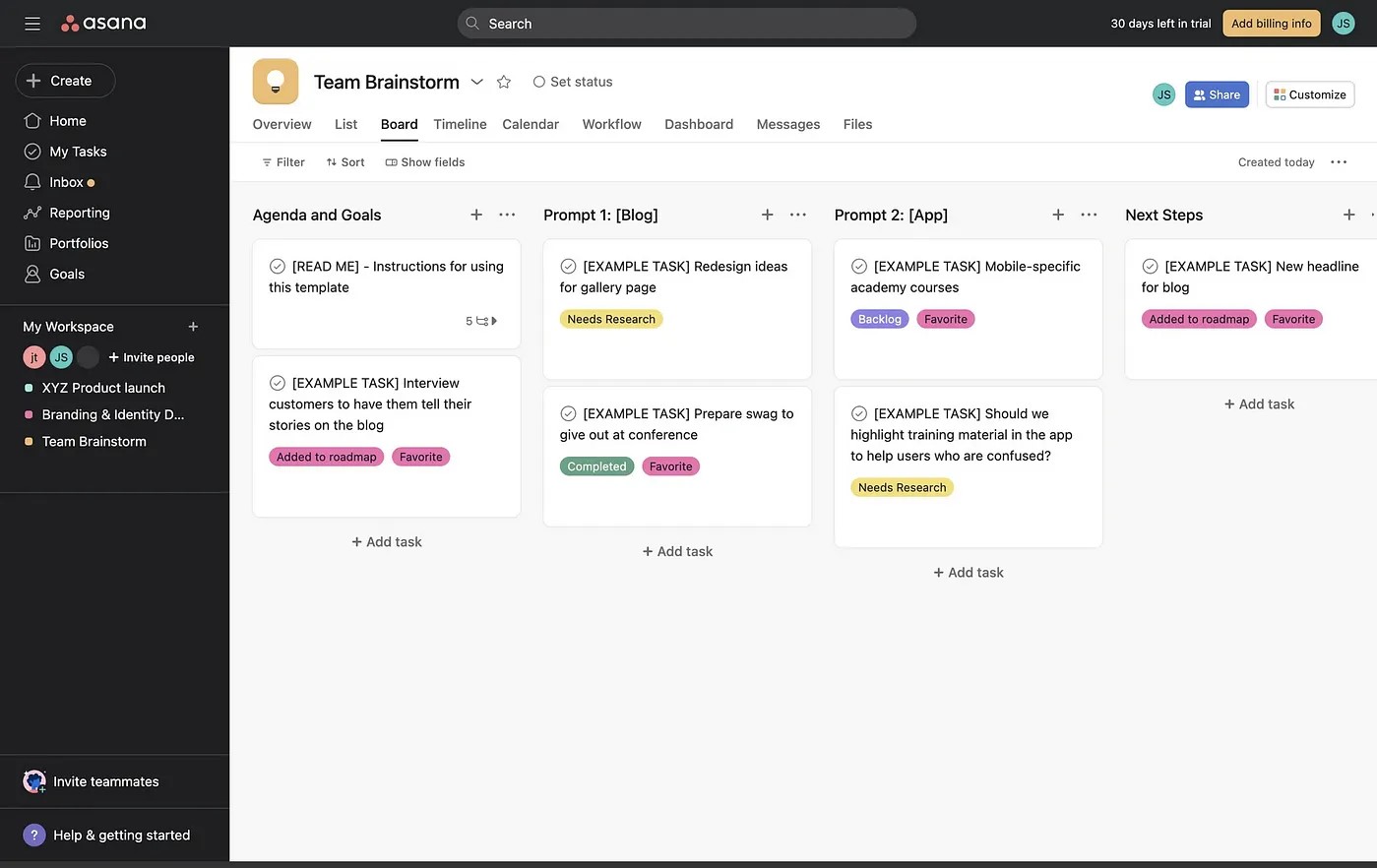
💠Content Strategy
- B2C Design: Content in B2C design is often concise, engaging, and persuasive. The aim is to quickly capture the user’s attention and guide them toward making a purchase or engaging with the brand. Storytelling, visuals, and emotional appeal are commonly used to create a connection with the audience. The content strategy revolves around highlighting the benefits, features, and lifestyle enhancements that the product or service offers.
- B2B Design: B2B content, on the other hand, is more detailed and informative. It often includes white papers, case studies, product specifications, and industry insights. The goal is to educate and inform the user, helping them make an informed decision. The content strategy in B2B design focuses on demonstrating the product’s value, ROI, and how it solves specific business challenges. The tone is more professional and straightforward, reflecting the serious nature of B2B transactions.
💠Design Aesthetics and Visual Hierarchy
- B2C Design: B2C designs are often vibrant, dynamic, and visually stimulating. The use of bold colors, creative typography, and high-quality imagery is common to create a memorable brand experience. Visual hierarchy is crucial, with calls-to-action (CTAs) prominently displayed to encourage quick user interaction. The design aesthetics in B2C are tailored to attract and retain the attention of the individual consumer, often incorporating trends and styles that appeal to the target demographic.
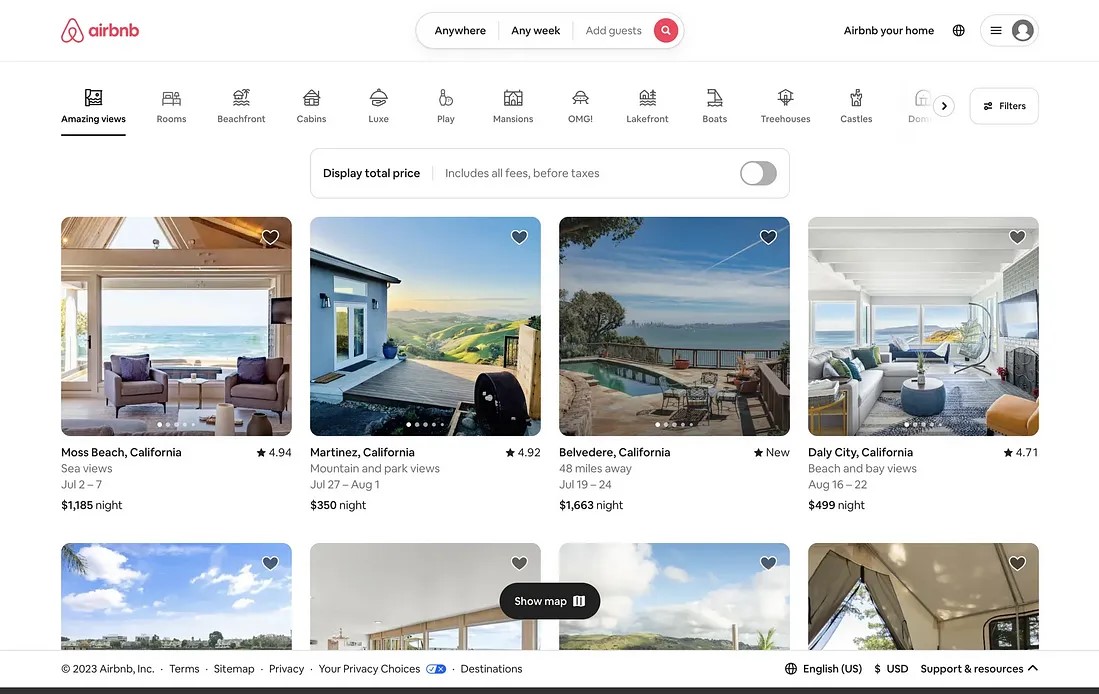
B2B Design: B2B design is generally more restrained and professional. The aesthetic is often clean, minimalistic, and focused on clarity. The visual hierarchy in B2B design prioritizes the presentation of information in a logical and accessible manner. The use of color is more subdued, and the emphasis is on readability and functionality rather than emotional appeal. B2B designs aim to facilitate ease of navigation, helping users find the information they need quickly and efficiently. 
💠User Experience (UX) and Functionality
- B2C Design: In B2C, UX is centered around simplicity, enjoyment, and speed. Consumers expect a seamless, enjoyable experience with minimal effort. Features like one-click purchases, personalized recommendations, and interactive elements are common in B2C designs. The focus is on creating a frictionless journey from discovery to conversion.
- B2B Design: B2B UX prioritizes efficiency, reliability, and scalability. Users in B2B contexts often require advanced features such as account management, integration with other business tools, and detailed reporting. The design must accommodate complex workflows and provide robust functionality that supports the business processes of the user. The user journey in B2B is typically longer and more involved, requiring careful consideration of each touchpoint.
💠Conversion Goals and Metrics
- B2C Design: Conversion goals in B2C design are usually straightforward, such as product purchases, sign-ups, or downloads. The metrics focus on immediate actions like click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer retention. B2C designs often include multiple touchpoints that guide users towards these conversion goals, using persuasive design techniques and emotional triggers.
- B2B Design: B2B conversion goals are more complex and often involve multiple stages, such as lead generation, nurturing, and final purchase. The metrics in B2B design may include lead quality, sales pipeline progression, and customer lifetime value (CLV). B2B designs are built to support long-term relationships and often incorporate features that facilitate ongoing communication and engagement with potential clients.
💠Branding and Trust
- B2C Design: Branding in B2C is about creating a strong emotional connection with the consumer. The design must reflect the brand’s identity, values, and personality, making it memorable and relatable. Trust is built through consistent messaging, high-quality visuals, and positive user experiences.
- B2B Design: In B2B, branding is more about credibility, expertise, and reliability. The design must convey professionalism and trustworthiness, often through a more conservative and consistent visual identity. Trust is built through clear communication, proven results, and industry recognition.
While both B2C and B2B design aim to engage users and achieve business goals, the approaches differ significantly due to the nature of the audiences and the objectives involved. B2C design is more about capturing attention and creating an emotional connection, whereas B2B design focuses on clarity, functionality, and fostering long-term business relationships. Understanding these differences allows designers to tailor their strategies effectively, ensuring that the design resonates with the intended audience and supports the overall business goals.
If you have any questions about your project, please write to us 🚀🚀🚀
We are happy to help🤝