Managing large arrays efficiently in PHP 8.3 is crucial for performance, especially when handling datasets that can grow into millions of elements. In this guide, we’ll explore key memory management techniques, including optimized data structures, built-in PHP functions, and external tools that help reduce memory footprint while maintaining performance.
📌 Step 1: Understanding How PHP Stores Arrays
PHP arrays are dynamic, associative, and hash-based, making them flexible but also memory-intensive. Each array element consists of a key-value pair, where PHP maintains an internal structure (a zend_array) to manage them. This overhead can add up quickly when dealing with large datasets.
Key Insights:
- PHP arrays consume more memory than simple indexed arrays in languages like C or Python.
- Each element requires additional metadata storage for keys and type information.
- Duplicating arrays or modifying them (copy-on-write) can unexpectedly increase memory usage.
📌 Step 2: Choosing the Right Data Structure
Instead of using standard PHP arrays for large datasets, consider alternatives that optimize memory usage:
Alternatives:
- SplFixedArray: A more memory-efficient structure for indexed arrays that reduces overhead.
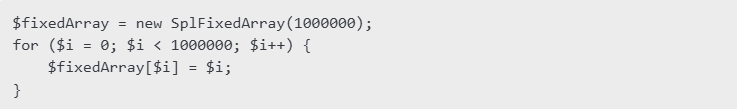
- Generators (Lazy Evaluation): Avoids loading large arrays into memory by yielding values on demand.

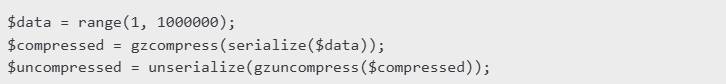
- Data Compression (gzcompress): Store large arrays in a compressed string format to save space.
📌 Step 3: Reducing Memory Footprint with PHP 8.3 Optimizations
PHP 8.3 introduces internal optimizations that reduce memory allocation, but you can still manually fine-tune memory usage:
Techniques:
⚡Use unset() to Free Memory
$largeArray = range(1, 1000000);
unset($largeArray); // Frees memory
gc_collect_cycles(); // Triggers garbage collection⚡Use Array Chunking
$chunks = array_chunk(range(1, 1000000), 10000);
foreach ($chunks as $chunk) {
processChunk($chunk);
}⚡Use Memory-Efficient Sorting (ksort() over asort())
ksort($largeArray, SORT_NUMERIC); // Uses less memory than asort()📌 Step 4: Profiling and Debugging Memory Usage
Use built-in PHP functions to monitor memory consumption:
memory_get_usage(true): Get current memory usage.memory_get_peak_usage(true): Identify peak memory consumption.xdebug_debug_zval('variable'): Inspect reference counts.
Example:

Managing large arrays in PHP 8.3 efficiently requires a combination of using the right data structures, leveraging lazy evaluation techniques, and actively profiling memory usage. By applying these strategies, you can significantly reduce memory consumption and improve application performance, making PHP a viable choice for handling large-scale data processing tasks.
Happy coding🚀




